How did the Cold War directly affect Latin American countries?
Subject(s): Economics, Latinos, World History, US History, and Geography
Time Period(s): (1945-Early 1970s) Postwar United States
Grade level(s): 9-12
Click here to download the PowerPoint
Supporting question(s):
Describe the relationships between the United States and Latin American countries during the Cold War.
Why did the United States become involved in Latin America?
What types of government did Latin American countries have after World War II?
What types of resources did Latin American countries have?
Source Set
- “The Red Outpost in Central America,” LIFE Magazine, October 1953
- Interview with Robert Corrigan
- Evening Star, November 6, 1962
- House Resolution 205, February 19, 1975
- Juan Bustamante Interview
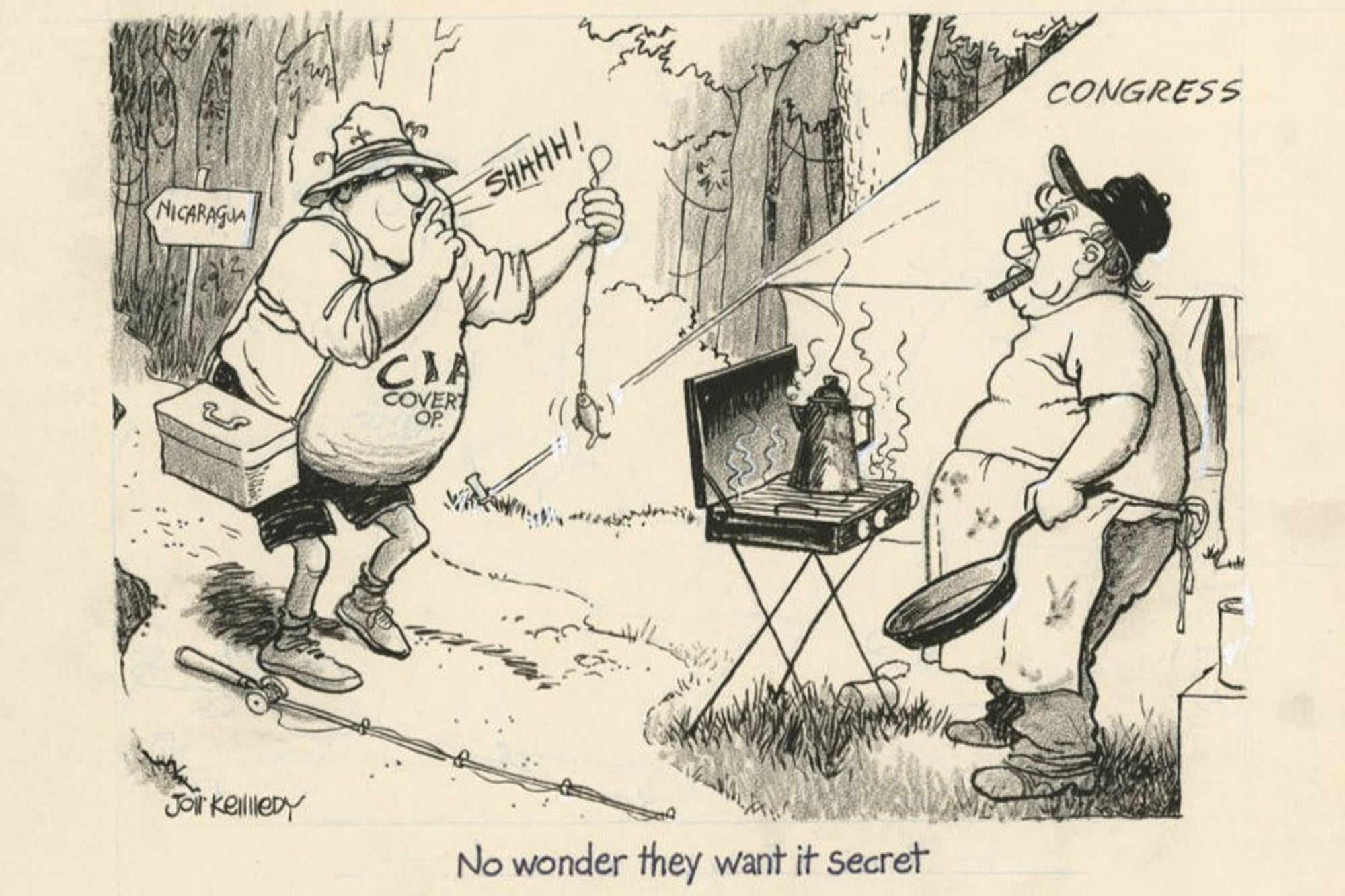
- No Wonder They Want it Secret
- Senator Daniel Inouye speech, March 27, 1986
Description
Resolution directing the Secretary of Defense to Provide Information, and answer certain questions, relating to American policy toward Chile between 1964 and 1974.
Description
2006 interview of Juan Bustamante, Chilean immigrant to the U.S., by his daughter Dafne.
Listen to clip from 5:15-10:20
Additional resource(s):
Truman Library lesson plan: U.S. Policy in Latin America during the Cold War
Retro Report: Cold War in Latin America
CSPAN American History TV summary of Iran-Contra Hearings
Arkansas Frameworks(s):
High School World History
H.6.WH.29
Analyze the change and continuity in global power after World War II, including the growing rivalry between Communist and democratic governments in various regions:
- Africa
- The Americas
- Asia
- Europe
- Middle East
World History standard
H.6.WH.32
Assess geographic, human, and economic costs of war using evidence from multiple sources and perspectives:
- Disease
- Famine
- Genocide
- Loss of natural resources
- Terrorism